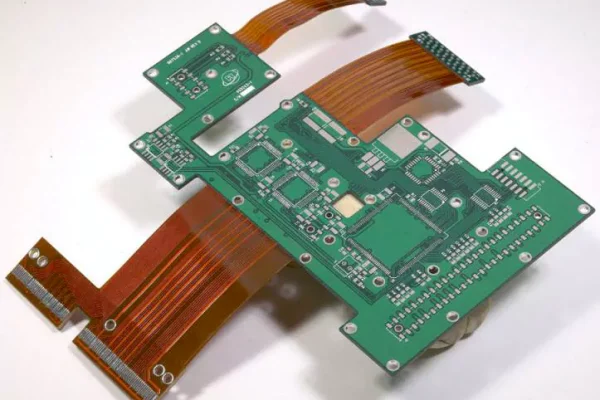
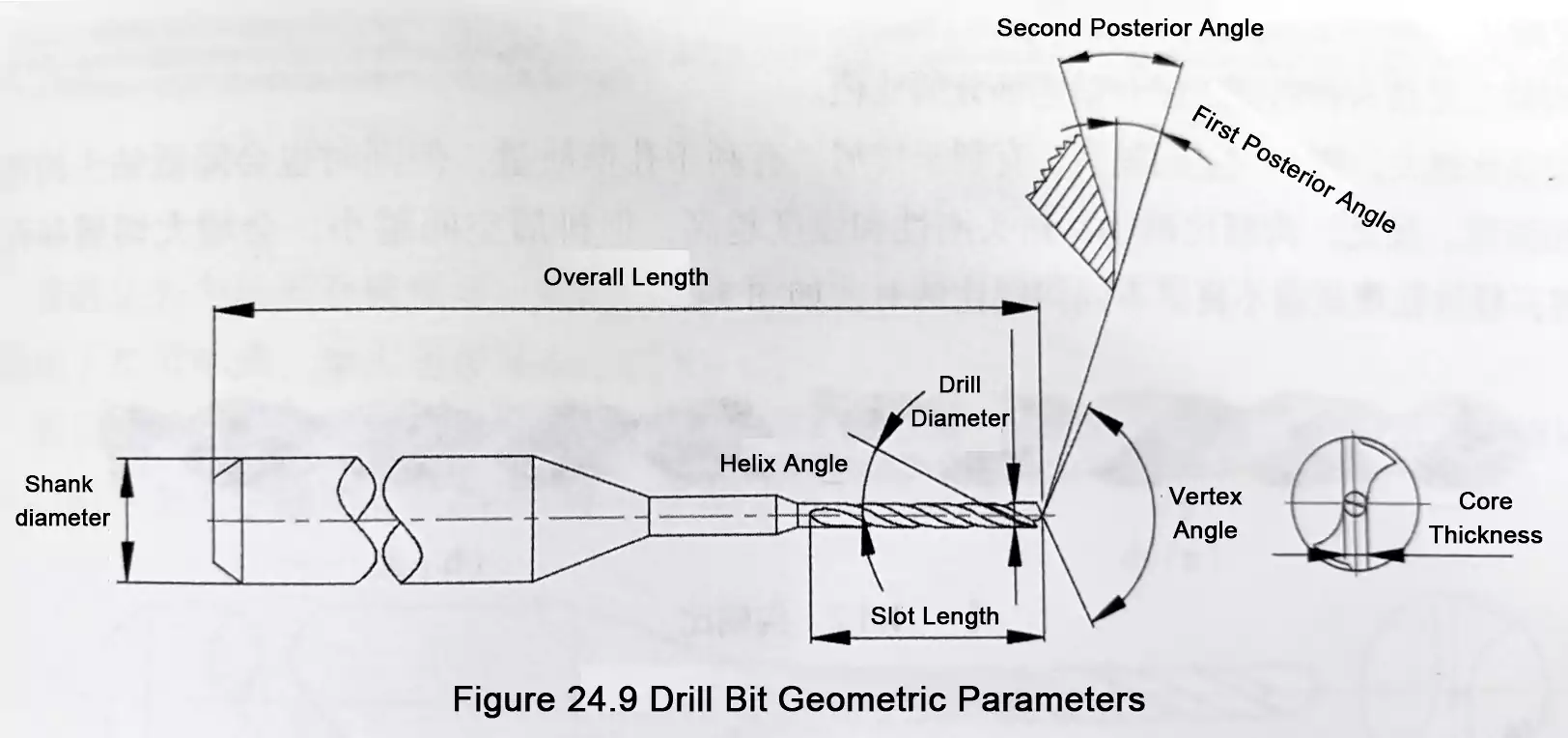
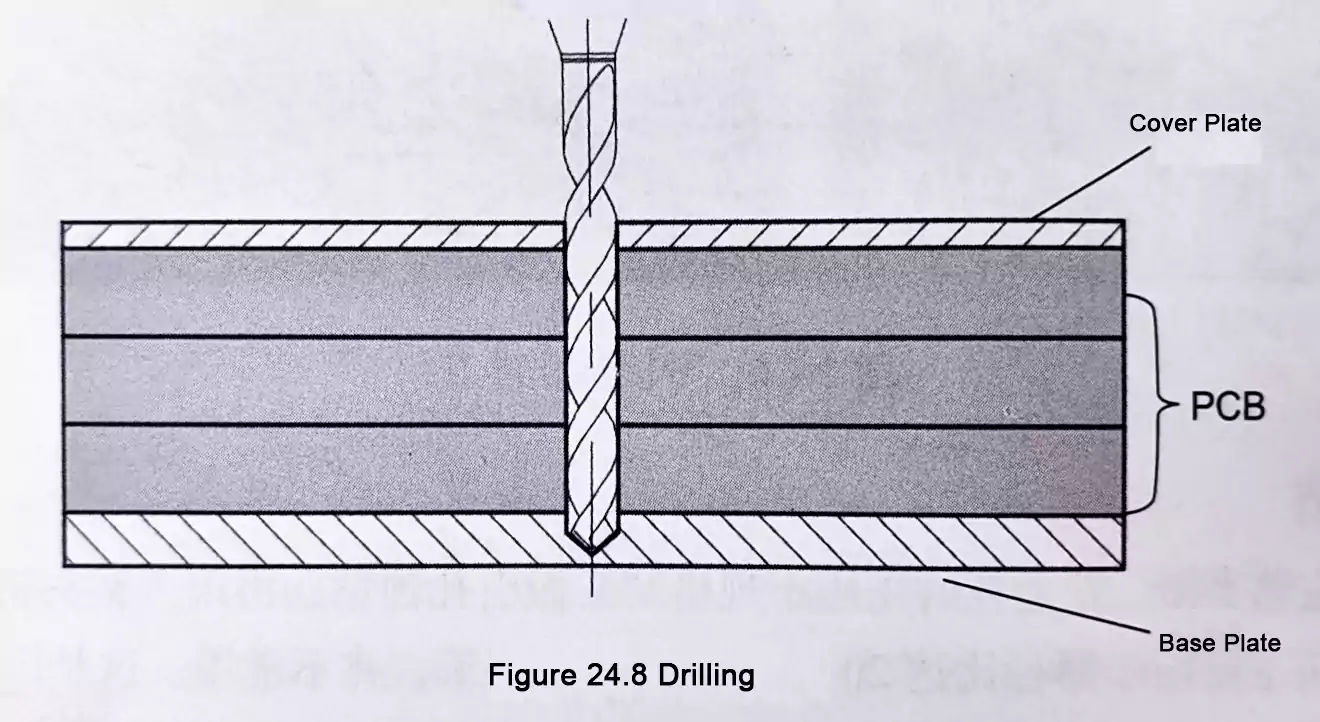
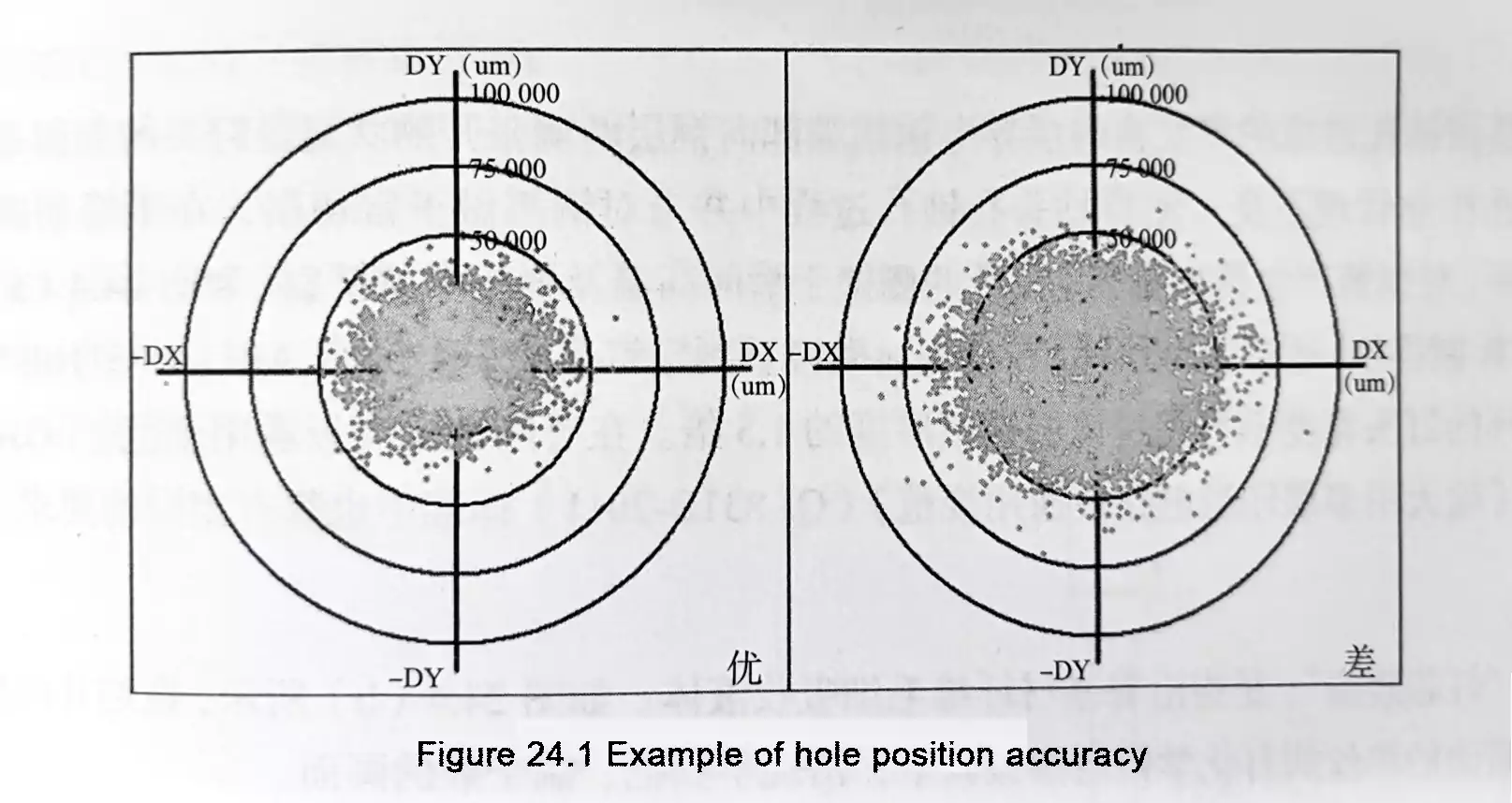
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in modern electronic products. Based on material and performance characteristics, PCBs are mainly categorized into two types: Rigid PCBs and Flexible PCBs (FPCs). These two types differ significantly in structure, functionality, and application. Choosing the right one is crucial to product performance and cost-efficiency.
Below are the key factors to consider when choosing between rigid and flexible PCBs:
Application Scenarios & Functional Requirements
Rigid PCBs: Ideal for applications requiring strong structural stability, high mechanical strength, and resistance to harsh environments. Common in consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and automotive systems.
FPCs: Best suited for compact, lightweight designs that require flexibility or dynamic bending. Common in wearables, foldable devices, cameras, and medical instruments.
Tip: Choose rigid boards for durability and FPCs when space, weight, and bending matter.
Product Design & Layout Complexity
FPCs enable three-dimensional wiring and can be folded or bent to fit tight or irregular spaces. They're ideal for designs where traditional wiring is limited.
Rigid PCBs work well in products with a fixed layout, where the circuit remains static and mechanical stress is minimal.
Tip: If the design involves movement or space constraints, FPCs offer more design flexibility.
Cost & Production Timeline
Rigid PCBs: Lower cost and shorter lead times. Suitable for mass production and standardized designs.
FPCs: Higher unit cost and longer production cycles due to complex manufacturing processes. Best for customized, low-volume applications.
Tip: For cost-sensitive or high-volume products, rigid PCBs are more economical.
Reliability & Maintenance
Rigid PCBs offer high durability and low maintenance over time, making them ideal for products with long life cycles.
FPCs, while flexible and lightweight, may face issues if bent repeatedly, affecting long-term reliability.
Tip: Evaluate bending frequency and reliability requirements before choosing FPCs.
Manufacturing Technology & Process
Rigid PCBs benefit from a mature and stable manufacturing process.
FPCs require advanced equipment and precision control due to the complexity of their structure.
Tip: Ensure your manufacturing partner has the technical capability and quality standards to produce FPCs.
Conclusion
Choosing between Rigid PCBs and Flexible PCBs depends on several factors:
Application needs
Design and space constraints
Cost and production scale
Reliability expectations
Manufacturing capabilities
By carefully evaluating these aspects, you can select the most suitable PCB type for your product, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.