Introduction
Laminates are the structural and electrical foundation of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Accurate pcb laminate identification is critical for material selection, manufacturing, inspection, and compliance.
While most engineers focus on properties like Tg, Dk, or CTE, ensuring the material actually meets IPC-4101 requirements is equally critical. This standard defines key parameters such as thickness tolerance, copper weight, foil type, and visual quality levels—all of which impact PCB performance and reliability.
This article outlines a practical, standards-based approach to laminate identification. You'll learn:
What IPC-4101 covers and how to read slash sheets
Key inspection criteria for verifying laminate compliance
A checklist for procurement and quality control
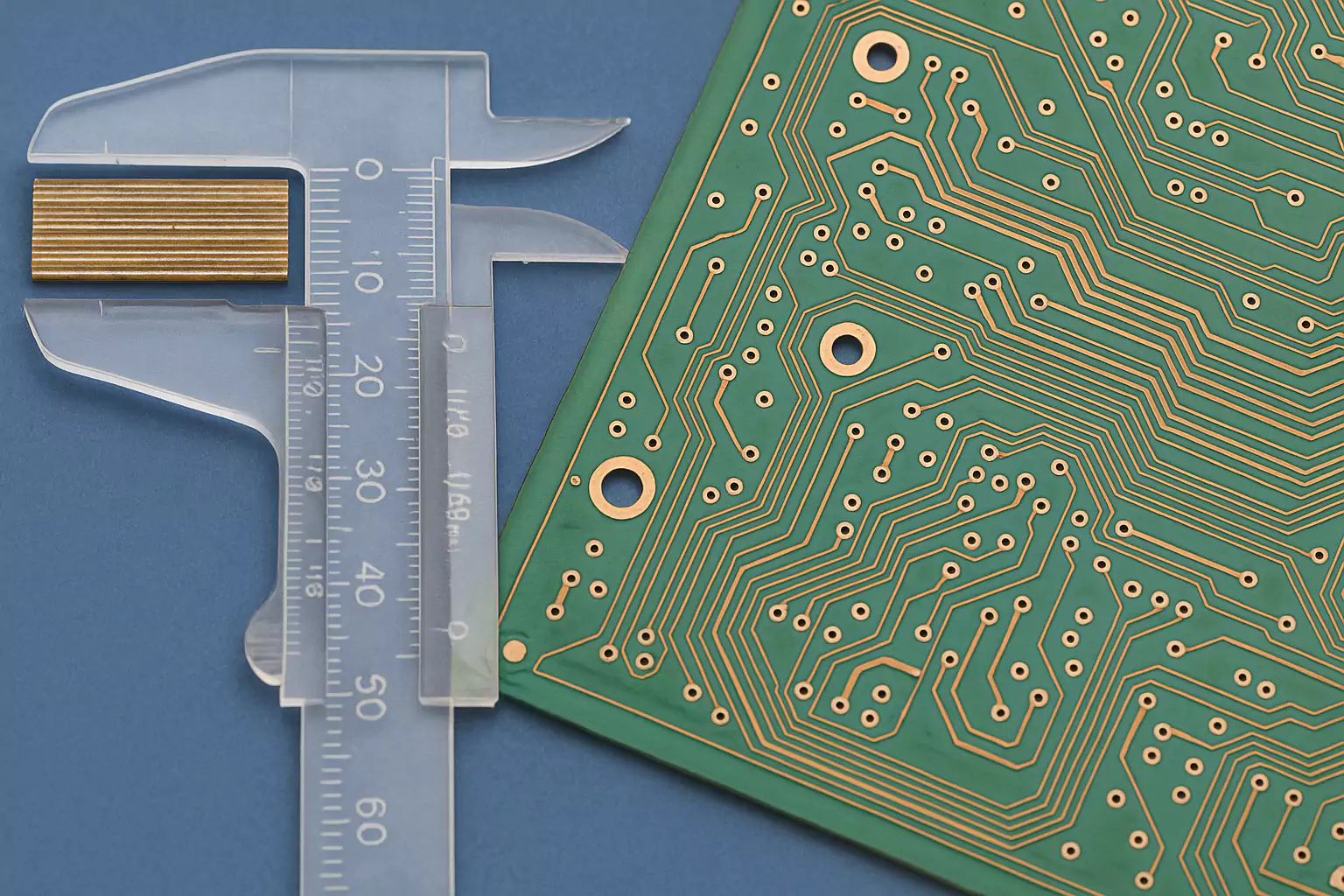
Standards and Terminology Overview
IPC-4101 is the primary international standard that defines performance requirements for laminate and prepreg materials used in rigid PCBs. It provides specifications for mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties to ensure consistent material quality and reliability.
What Is IPC-4101?
IPC-4101 helps manufacturers and designers:
Select suitable laminate materials for different applications.
Ensure materials meet baseline quality and performance standards.
Support compliance with thermal, electrical, and environmental requirements.
IPC Slash Sheets Explained
A unique feature of IPC-4101 is the slash sheet system (e.g., /21, /126, /129), which identifies specific material types based on:
Resin system and filler content
Glass fabric reinforcement
For example:
IPC-4101/21 refers to a typical FR-4 epoxy laminate with mid-range Tg.
Using slash sheets ensures precise material identification and avoids confusion that can arise from generic terms like "FR-4."
Key Terms to Know
Understanding the following parameters is essential when identifying or verifying PCB laminates:
Tg (Glass Transition Temperature): Indicates thermal stability during soldering.
Td (Decomposition Temperature): Shows the material's thermal limit before breakdown.
CTE (Coefficient of Thermal Expansion): Affects dimensional stability during temperature changes.
Dk (Dielectric Constant) & Df (Dissipation Factor): Crucial for signal integrity in high-speed and RF PCBs.
Copper Foil Weight: Typically 1 oz = ~35 µm; impacts current capacity and heat dissipation
Key Criteria for Identifying PCB Laminate Material
Proper identification of PCB laminate materials is essential for ensuring performance, reliability, and IPC compliance. Based on IPC-4101, here are the key criteria used in manufacturing and inspection.
- Material Thickness and Tolerance
IPC-4101 defines standard thickness tolerances for different grades (A, B, C, D). For example:
0.120–0.164 mm:
Grade A: ±0.038 mm
Grade B: ±0.025 mm
Grade C: ±0.018 mm
Tight control of thickness ensures consistent impedance and stack-up reliability.
- Copper Foil Weight and Thickness
Copper is specified by weight (oz/ft²), with 1 oz ≈ 34.3 µm. IPC-4101 lists common weights from 0.5 oz to 14 oz. Accurate measurement is critical for current capacity and thermal performance.
- Foil Type and Surface Treatment
IPC-4101 classifies copper types (A–Z), indicating treatment methods:
Type A: Rolled, annealed copper
Type H: Electrolytic, flame-treated
Type Y/Z: High ductility, dual-treated for embedded components
Foil type affects etching, adhesion, and reliability in fine-line or HDI applications.
- Visual Quality Grade
Surface quality is graded (A–D) by defect count over a 50×50 mm area:
Grade A: ≤ 29 points
Grade D: 0 defects (used in high-reliability PCBs)
10× magnification is typically used for inspection.
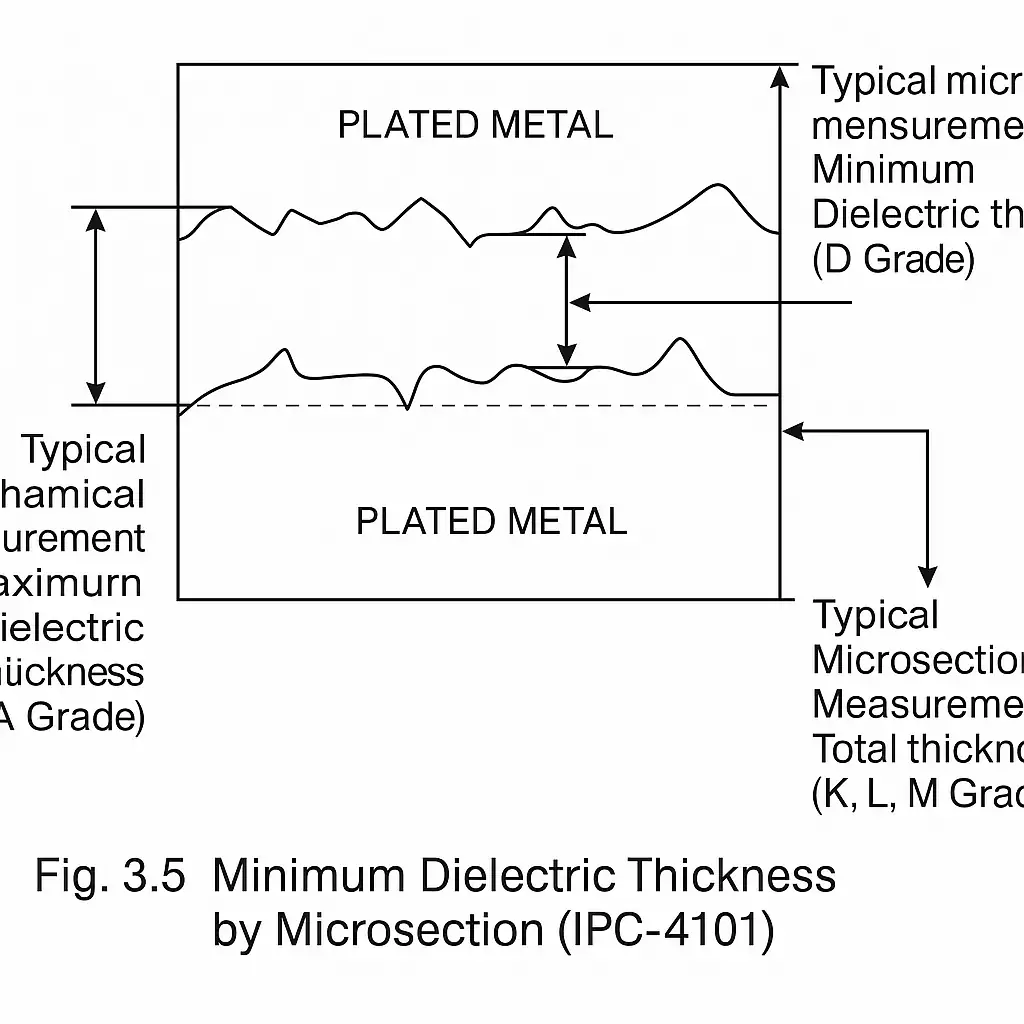
- Dielectric Thickness (Microsection Measurement)
Minimum dielectric thickness is verified via microsectioning, especially for HDI or impedance-controlled layers. IPC-4101 defines methods and acceptable limits.
- Slash Sheet Identification
Every IPC-4101-compliant material is identified by a specific slash sheet number (e.g., IPC-4101/21, IPC-4101/126). These slash sheets define the exact resin system, filler content, Tg, Td, and other performance metrics.
Laminate Identification Checklist Based on IPC-4101
| Check Item | Action Required | Reference | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Slash Sheet Confirmation | Confirm IPC-4101 slash sheet number is specified and traceable | IPC-4101 spec | Must match required material class (e.g., /21, /126) |
| 2. Thickness Measurement | Measure core/prepreg thickness using micrometer or optical tool | Table 3.6 (IPC-4101) | Use correct tolerance class: A/K, B/L, C/M, or D |
| 3. Copper Foil Weight | Check copper thickness based on weight per area (e.g., 1 oz ≈ 35 µm) | Table 3.5 (IPC-4101) | Confirm both thickness and foil uniformity |
| 4. Foil Type Validation | Identify foil category (annealed, ED, reverse-treated, etc.) | Table 3.4 + IPC-4562 | Foil type affects etchability, flexibility, and thermal stability |
| 5. Visual Surface Quality | Inspect 50mm × 50mm area at 10× magnification; count visible pits/dents | Table 3.8 (IPC-4101) | Grade A: ≤29 pts, B: ≤17, C: ≤5, D: 0 |
| 6. Cross-Section Analysis | Conduct microsection to verify dielectric & copper thickness | Figure 3.5 (IPC-4101) | Useful for high-reliability or multilayer inspection |
| 7. Documentation & Traceability | Record inspection results and link to material batch/lot | Internal QA documentation | Supports audits and failure analysis |
Conclusion
Proper identification of PCB laminate materials ensures compliance with IPC-4101 standards and supports consistent product quality. Key factors such as thickness tolerance, copper foil type, surface quality grade, and slash sheet compatibility must be verified during procurement and inspection.
By following a structured checklist, manufacturers and engineers can reduce risk, prevent defects, and ensure reliable PCB performance. Effective laminate identification is not just about choosing materials—it's about validating them at every stage of production.