Top 6 Advantages of Using Flexible PCBs in Product Design
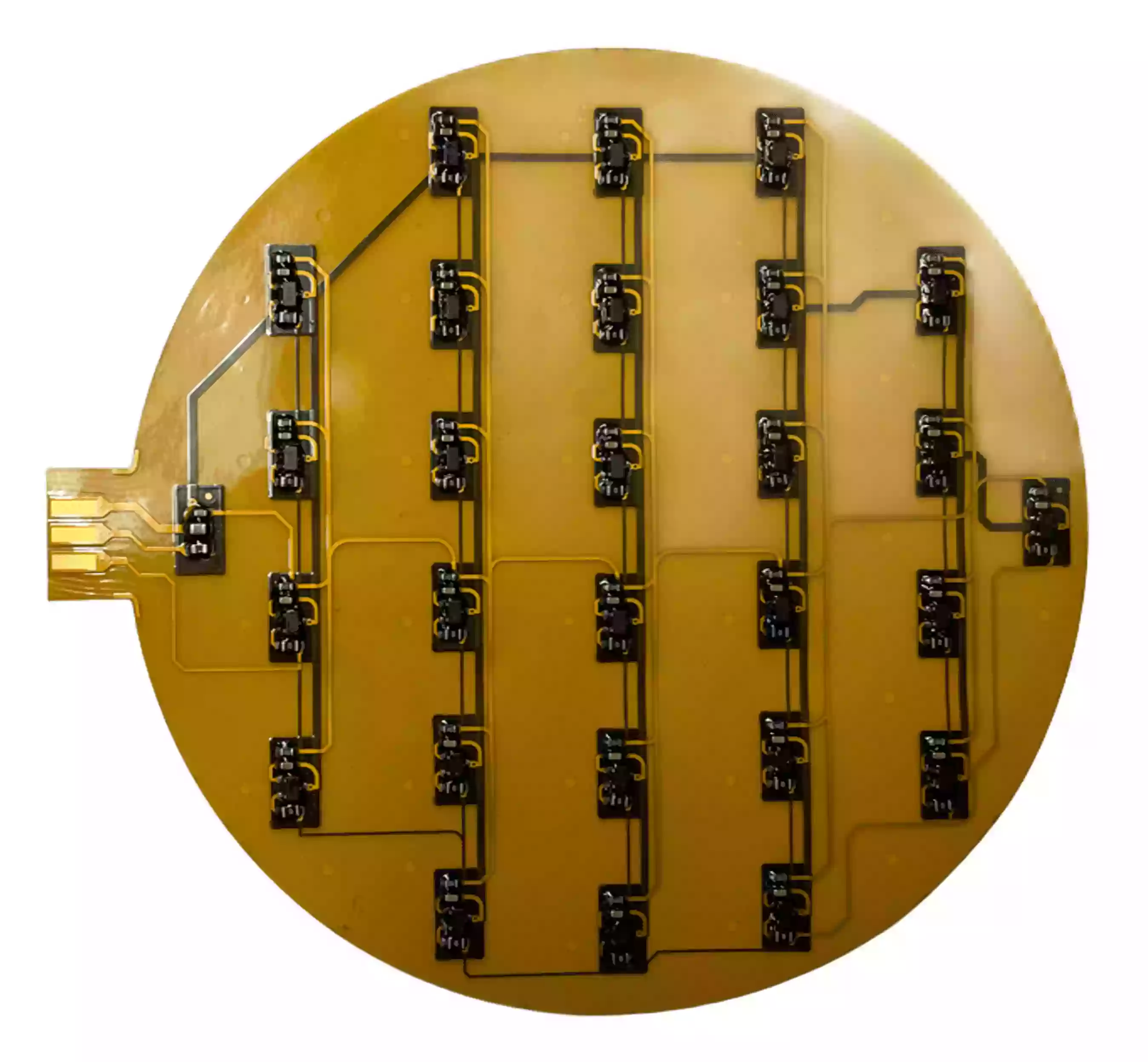

As technology advances, so does the demand for smaller, lighter, and more efficient devices. Engineers and designers are turning to Flexible Printed Circuits (FPCs) to meet these evolving demands. In this article, we explore the top six advantages of using flexible PCBs in product design and how they can significantly improve your projects.
What Is FPC? The Ultimate Guide to Flexible Printed Circuits
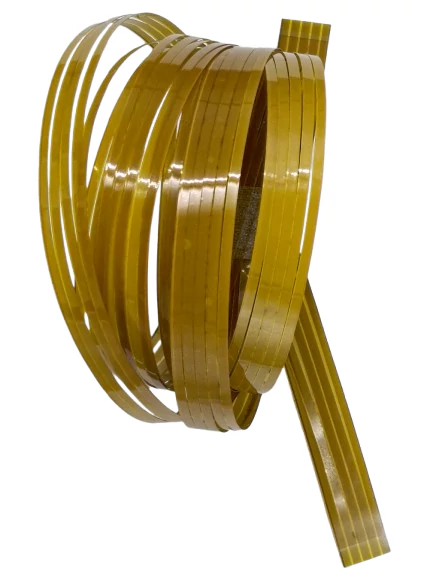

In today’s rapidly evolving electronics industry, innovation drives the need for smaller, lighter, and more efficient devices. Flexible Printed Circuits (FPC), also known as flexible PCBs, are essential to this advancement. These highly adaptable circuits allow for complex electronic designs in compact spaces. But what exactly are FPCs, and why are they so important? In this guide, we’ll dive into the details of FPC technology, its applications, and the key benefits it offers.
FPC Flexible PCB vs. Rigid PCB: How to Choose the Best PCB for Your Project
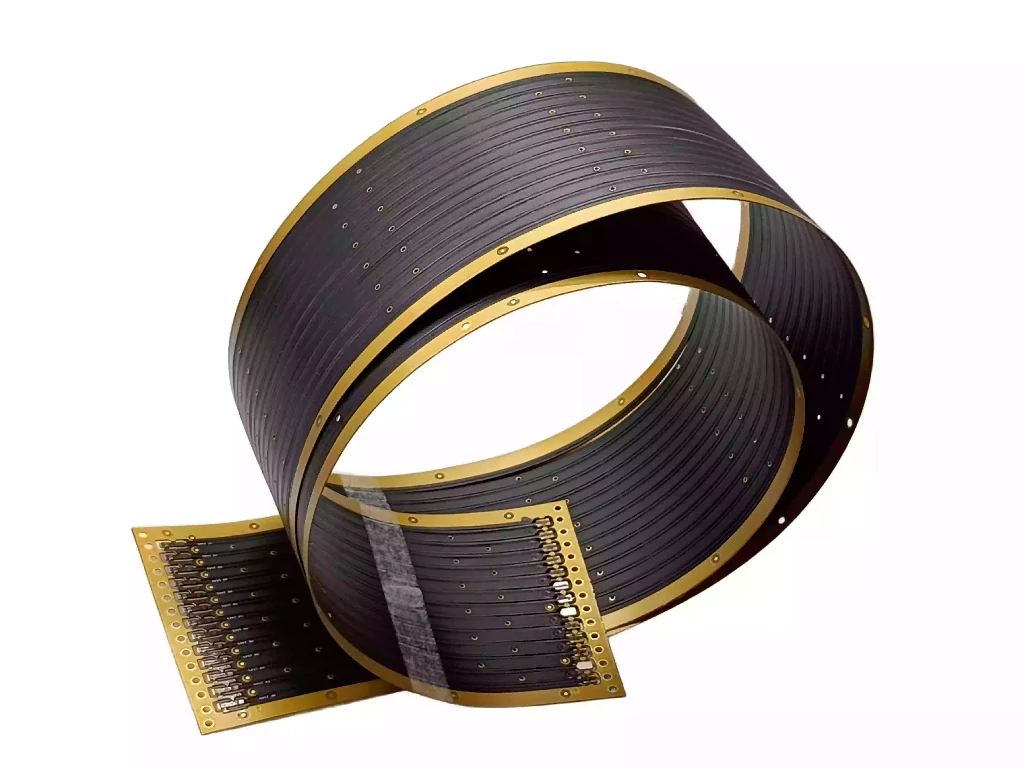

When designing modern electronic products, selecting the right type of PCB—FPC soft board or rigid PCB—is crucial for performance, reliability, and product innovation. In this blog, we’ll focus on the benefits and use cases of FPC flexible PCBs, and offer guidance on how to choose between flexible and rigid options depending on your needs.
Key SMT Process Requirements for Industrial Control Boards: A Comprehensive Guide
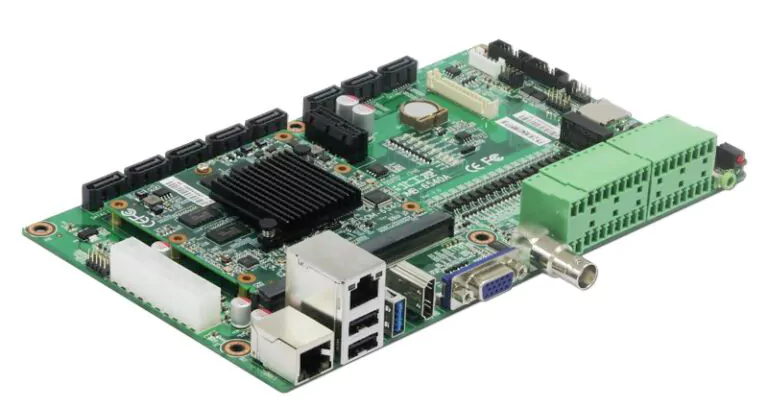

Industrial control boards are the core components of automation systems, acting as the "brain" of industrial equipment. Their performance and reliability are critical to overall system stability. The Surface Mount Technology (SMT) process used in manufacturing these boards demands high precision and stringent quality control. This article explores the essential SMT process requirements for industrial control boards across every production stage.
The Importance of a BOM Table in PCBA Processing: A Complete Guide to Procurement and Production Efficiency
In the world of Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA), the Bill of Materials (BOM) table plays an essential role throughout the manufacturing process. Serving as the backbone of component procurement, production planning, quality control, cost management, and maintenance, a well-structured BOM ensures that everything runs smoothly from start to finish.
Immersion Gold vs. Tin Spraying (HASL) in PCB Manufacturing: A Complete Comparison
When it comes to PCB surface finishes, choosing the right process is critical to ensure performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Among the most widely used surface treatments in PCB manufacturing are Immersion Gold (ENIG) and Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL), often referred to as tin spraying. While both serve to protect the exposed copper and enhance solderability, they differ significantly in terms of process, performance, cost, and application.
PCB Stack Design Explained: Optimizing Performance, Cost, and Reliability
PCB stack design is an important step before circuit board layout design, which involves the arrangement of copper and insulation layers that make up the PCB. Through reasonable stack design, the performance, reliability, and cost of the circuit board can be ensured to achieve the best balance.
Analysis of PCBA Process Flow
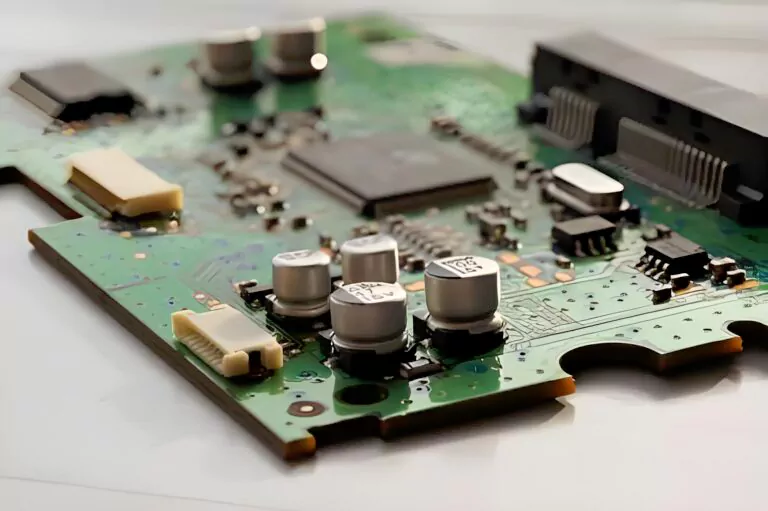

PCBA process=SMT processing process+DIP processing process.
According to different production technologies, PCBA has various process flows, including single-sided mixed assembly process, single-sided DIP insertion process, single-sided SMT mounting process, single-sided mounting and double-sided mixed assembly process, double-sided SMT mounting process and insertion mixing process, and so on. There are certain process differences in different manufacturing processes. Below is a detailed explanation of each process:
The difference between wave soldering and reflow soldering
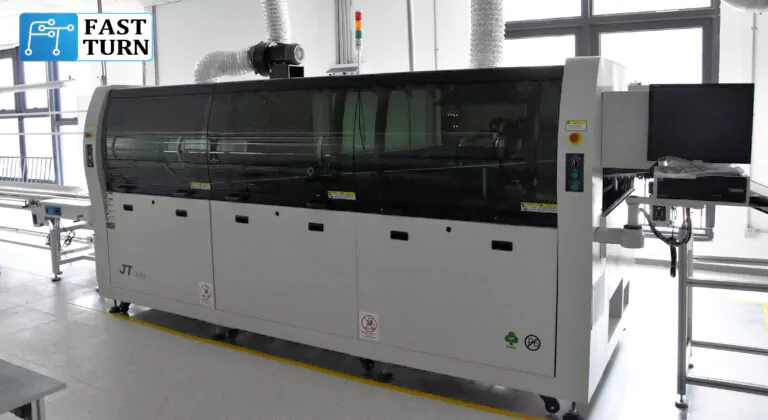

Wave soldering and reflow soldering are two commonly used soldering techniques in the electronic manufacturing industry, which have significant differences in principles, applications, functions, and other aspects.
Principles and Process Analysis of SMT Technology
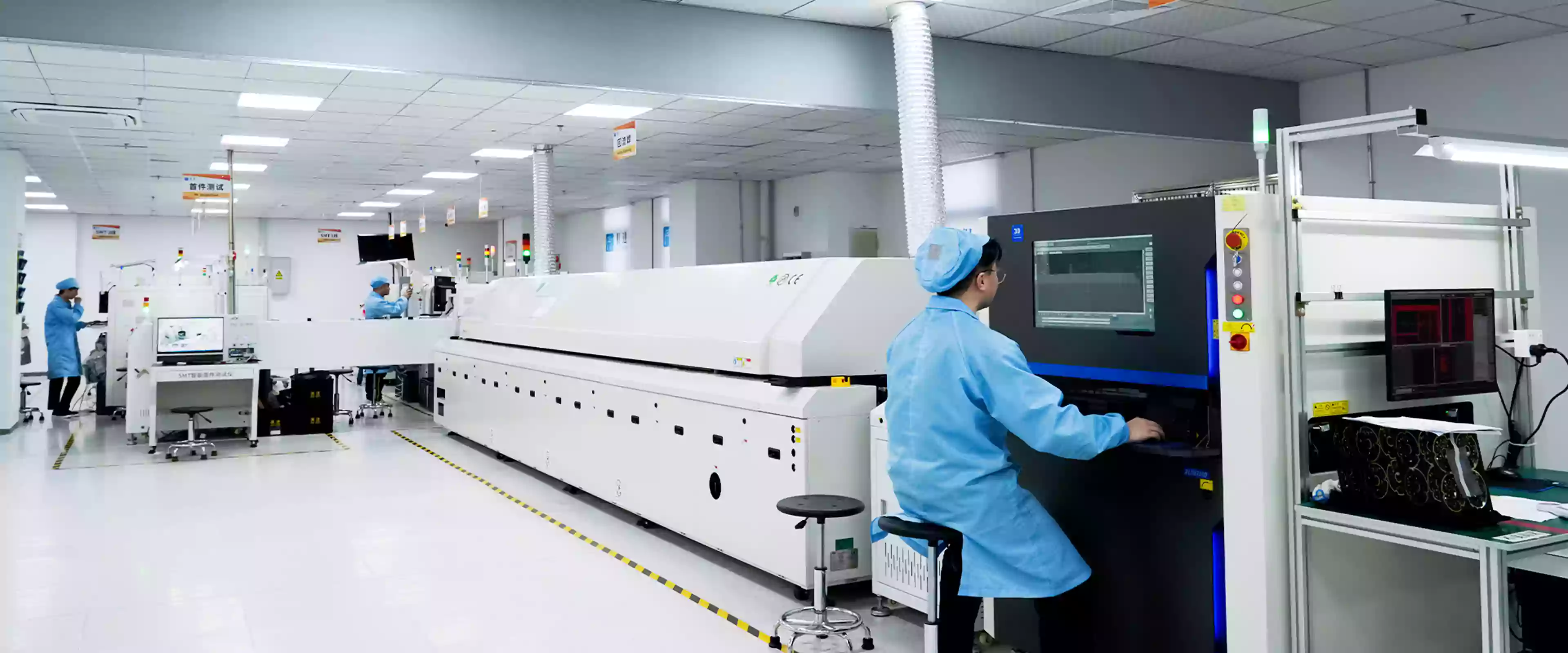

SMT, with its efficient and high-density characteristics, has become a key technical support for the miniaturization and high performance of modern electronic products. Below, we will analyze the core operating mechanism of SMT from three dimensions: technical principles, core processes, and key links.
Detailed explanation of PCBA production process
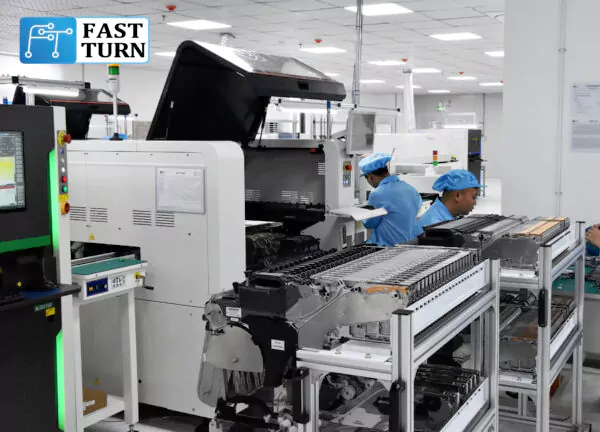

PCBA is one of the core components of the electronic manufacturing industry, involving multiple complex process steps and precise technical operations.
The production process of PCBA includes project evaluation and PCB board design, component procurement and inspection, solder paste printing and surface mount processing, reflow soldering and plug-in, wave soldering and cleaning, assembly, testing and packaging processes.
What are the reliability tests for PCB boards?
The reliability testing of PCB boards is a complex and rigorous process, covering multiple aspects such as soldering quality, functionality, environmental adaptability, and specialized testing. By selecting testing items and standards reasonably and applying and executing them according to the correct process, the quality and performance of PCB boards can be ensured to meet the highest standards.
